A healthy-looking body seems to be a goal many of us aspire to achieve. But what will a rowing machine help for muscle toning?
Nowadays, more and more people are choosing a rowing machine for cardio training at home. We almost forget that it’s also an ideal device to strengthen muscles. Read on to discover 5 facts about rowing machine muscle toning. It will help you understand and better reap the benefits of rowing machine in terms of muscle conditioning.
Table Of Contents
- Fact#1: Can You Use a Rowing Machine for Muscle Toning
- Fact#2: Why Using a Rowing Machine for Muscle Toning
- Fact#3: Main Muscles Used While Rowing
- Fact#4: If You Have Body Fat, Can You Get the Muscle Toning Result with a Rowing Machine
- Fact#5: Reap the Muscle Toning Result with a Healthy Diet
- Final Thought
Fact#1: Can You Use a Rowing Machine for Muscle Toning
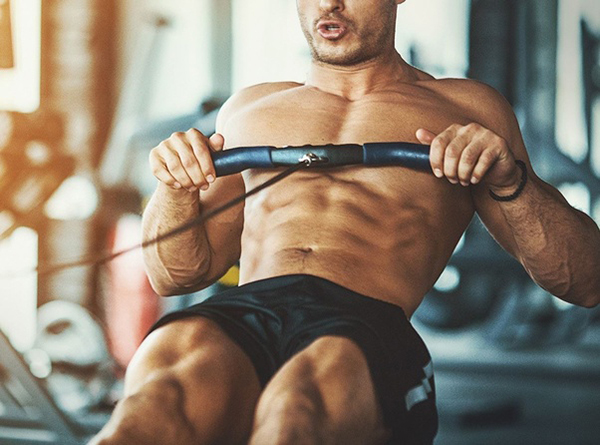
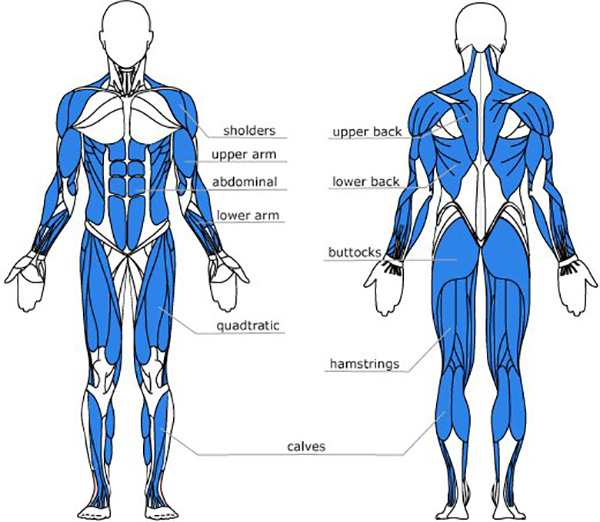
According to the English Institute of Sport, the rowing machine engages 86% of the muscles in your body. It activates the abs, back, shoulders, chest, triceps, wrists, glutes, hamstrings, and calf muscles.
As per the US Rowing, the national governing body of the United States of America in the sport, rowing is one of the few exercises that use major muscle groups from all parts of the body. If you’re focusing on burning fat and strengthening your muscles, rowing will not let you down.
Look at the muscles of a regular rower. That will convince you.

Fact#2 Why Using a Rowing Machine For Muscle Toning
If you want to tone your muscles, you need to add the rowing machine to your workout routine!
The rowing machine is great for toning your body as it’s an aerobic workout that uses all of the major muscle groups. Shedding excess fat is a huge part of toning your muscles, and the rowing machine has that covered! The less fat you have, the more your muscles can be seen making them appear more toned.
Besides, rowing is also a kind of resistance training that will help to strengthen your muscles. Combined with shedding fat, it makes your muscles appear toned and more defined.
To get the most out of the rowing machine benefits for shedding excess fat and toning your muscle, try using the rowing machine as part of a HIIT workout, like this one from the Coach Shane Farmer.
As we all know, the rowing machine is a piece of fitness equipment that mimics the motion of rowing a boat in the water. Let’s get a quick glance at the biomechanics of rowing, helping you understand why the rowing machine is a great full body exerciser for muscle toning.
Fact#3: Main Muscles Used While Rowing
What will the rowing machine do for you in terms of muscle toning? As an almost perfect piece of whole-body workout, the rowing machine muscles targeted are quads, hamstrings, calves, glutes, lats, core, shoulders, triceps, back, biceps.
Let’s get a quick glance at the biomechanics of rowing, helping you understand why the rowing machine is a great full body exerciser for muscle toning.
There are four key components to the basic rowing stroke: the catch, the drive, the finish, and the recovery. The basic rowing action is a coordinated muscle action that requires the application of force in a repetitive, maximal, and smooth manner. Every large muscle group will contribute to this action.
Dr. Thomas Mazzone conducted a more detailed analysis of the muscles used during each movement of a single rowing stroke, refer to the images below:
- The Catch
- The Drive -leg emphasis -body swing emphasis -arm pull through emphasis
- The Finish
- The Recovery
The Catch
- Deltoids
- Trapezius
- Serratus Anterior
- Erector Spinae
- Rectus Abdominus
- Hamstrings
- Triceps Brachii
- Tibialis Anterior
- Gastrocnemius
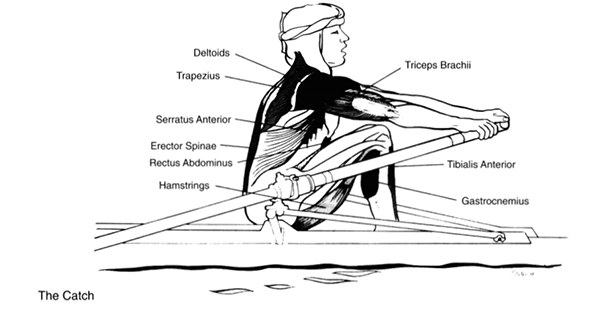
The erector spinae muscles of the back are relaxed to allow for trunk flexion, which is provided by the abdominals.
The psoas major and minor and the iliacus flex the pelvis and hips. The sartorius muscle rotates the thighs, allowing the body to flex between the thighs to obtain maximum reach.
The hamstrings and gastrocnemius are contracting while the knees are in flexion. The quadriceps are elongated and stretched, yet the rectus femoris is contributing to hip flexion. The ankles are dorsiflexed by the tibialis anterior.
The elbows are extended by the triceps brachii. The grip on the handle is accomplished by the flexor muscles of the fingers and thumb.
The Drive
The Drive – Legs Emphasis
- Deltoids
- Trapezius
- Teres Major
- Serratus Anterior
- Quadriceps
- Hamstrings
- Gluteus Maximus
- Gastrocnemius
- Soleus
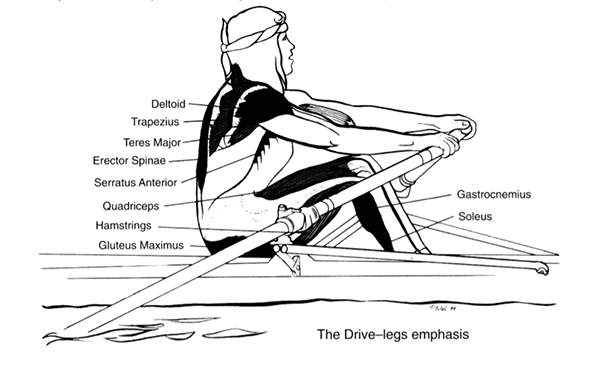
The initial portion of the drive demands maximal power from the legs.
The quadriceps extend the knee, and the feet are plantar flexed by the soleus and gastrocnemius muscles. A number of stabilizing muscles aid in supporting the lower back.
All the muscles of the shoulder are contracting. These include the supra and infraspinatus, subscapularis, teres major and minor, and the biceps brachii. The scapula is stabilized by the serratus anterior and trapezius muscles.
The Drive – Body Swing Emphasis
- Brachialis
- Erector Spinae
- Quadriceps
- Gluteus Maximus
- Hamstrings
- Biceps BraHamstringschii
- Brachioradialis
- Gastrocnemius
- Soleus
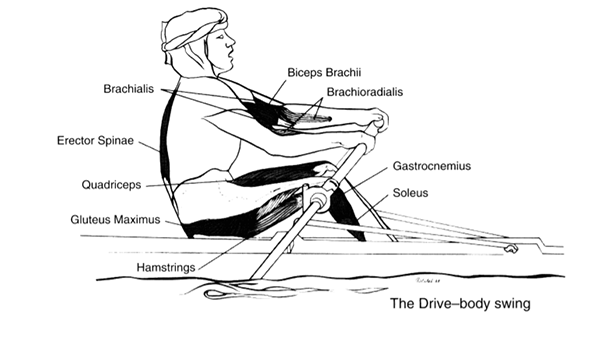
As the knees are finishing their extension, the hip is also extending by the contraction of the gluteus and hamstring muscles. Back extension is occurring by contraction of the erector spinae.
In the upper body, elbow flexion is occurring via the biceps, brachialis, and brachioradialis muscles.
The Drive – Arm Pull Through
- Trapezius
- Posterior Deltoids
- Teres Minor
- Brachialis
- Brachioradialis
- Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
- Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Pectoralis Major
- Biceps Brachii
- Quadriceps
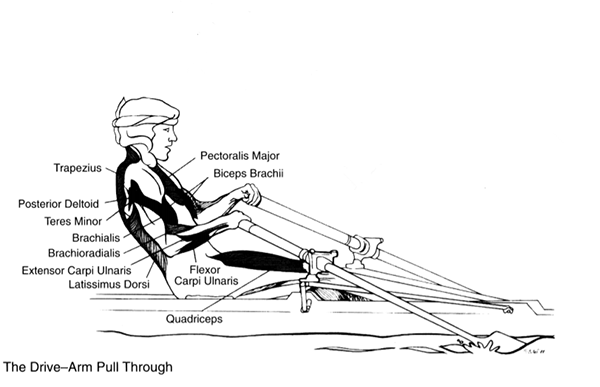
The knees are maximally extended, and the ankles are plantar flexed. Besides, hip and back extension are being completed.
The upper body musculature is contracting with high force to finish the drive. The elbow flexors are dominant. The flexor and extensor carpi ulnaris muscles of the forearm contract to stabilize and adduct the wrist. The shoulder is extended and adducted. The upper arm is internally rotated by the latissimus dorsi and pectoralis major. The teres minor, posterior deltoid, and long head of the biceps are acting on the shoulder joint. The scapula is rotated downward by the pectoralis minor and then drawn backward by the trapezius and rhomboid muscles.
The Finish
- Trapezius
- Posterior Deltoids
- Brachialis
- Biceps Brachii
- Brachioradialis
- Gluteus Maximus
- Latissimus Dorsi
- Forearm Extensors
- Quadriceps
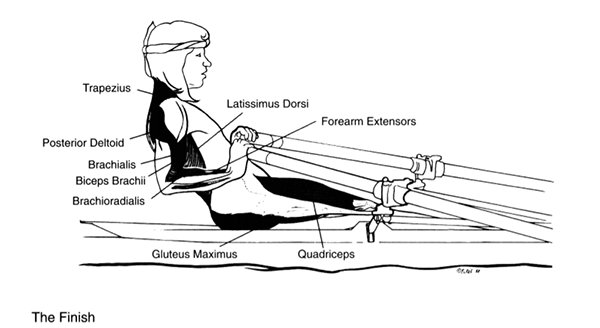
The knees and ankles remain constant as the hips complete a full extension. The back extensors are continually contracting, and the upper arms are internally rotated by the contracting latissimus dorsi. The triceps are extending the elbows slightly.
The Recovery
- Trapezius
- Rectus Abdominus
- Hamstrings
- Anterior Deltoid
- Triceps Brachii
- Wrist Extensors
- Gastrocnemius
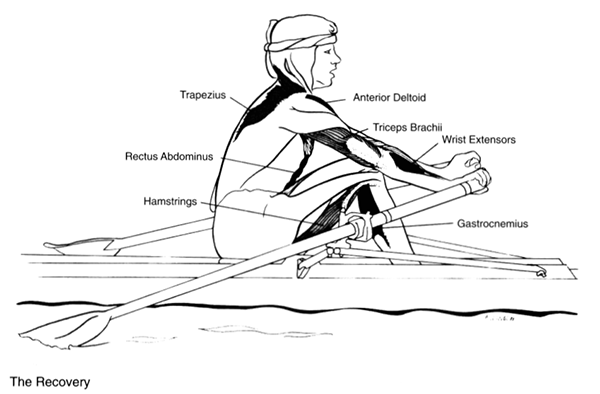
The arms are pushed forward and away from the body by the triceps until the elbows reach full extension.
The anterior deltoids contract along with the coracobrachialis, the biceps, and the upper arms raise slightly as they pass over the extended knees.
The abdominals flex the torso, and once the hands have cleared the extended knees, the slide begins its forward motion through ankle dorsiflexion and hip and knee flexion.
As you can see the rowing muscles used during the 4 phases are just about EVERY muscle in the body! No wonder rowing machines are famed for giving full-body workout!
Fact#4 If You Have Body Fat, Can You Get the Muscle Toning Result with a Rowing Machine?
The answer to this question depends on how you define “toning”.
Body fat is a factor when it comes to muscle toning. If the layer of fat (and other tissue) over a muscle is great enough, it will obscure the muscle and there won’t be tone or definition. If that same person, with no change in muscle, were to decrease their body fat, they would have greater definition.
So if you consider a toned body to simply be one with defined muscles, maintaining a low level of body fat (likely by way of a healthy diet) is key.
Fact#5: Reap the Muscle Toning Result with a Healthy Diet.

5.1 Eat 3 servings of lean protein a day for muscle toning.
Protein is an essential part of a healthy diet. It helps you feel full and repairing, regenerating, and building muscle.
Lean protein sources such as chicken, fish, and tofu are lower in fat than other sources of protein and give you the protein your body needs without the extra calories and fat, which means they’ll help you shed the extra weight and keep your muscle definition.
Choose 1 protein source for each meal, and make it a lean one.
If you’re regularly active and trying to tone up, aim for 1.2-1.7g of protein per Kg of body weight a day, if you’re trying to build muscle mass 1.8-2.4g per Kg will help you further.
5.2 Add a serving of fresh fruits or vegetables to each of your meals.
Fresh vegetables that are grilled, steamed, or boiled are low in calories and don’t have any extra fat from oils or additives from processing. Fresh fruits are full of vitamins and nutrients that will give your body the micronutrients it needs. They’ll also help you feel full so you’re less likely to overeat or snack on unhealthy foods, which will help you lose weight and reveal your muscles.
Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, and leafy greens will give your body healthy nutrients without extra calories.
Fruits like bananas, strawberries, and apples for a healthy snack option will give you a steady source of energy without any empty calories.
Fill up on fresh fruit and veggies will help you burn fat and improve muscle tone.
5.3 Eat healthy fats to complete a balanced diet for muscle toning.
Fats are often seen as a negative thing, but they’re actually super important for a healthy, balanced diet that will help you improve muscle tone.

The key is to choose healthy, monounsaturated fats like avocados and olive oil, as well as polyunsaturated fats from sources like salmon, tuna, and sardines. Adding a serving to at least 1 of your meals each day will make sure you’re giving your body everything it needs to build and maintain muscle.
Fatty fish will also add omega-3 fatty acids to your diet. These are healthy fats that help with inflammation, metabolism and improve heart and brain health.
Besides, you should limit saturated fats like butter, cheese, and fried food in your diet.
5.4 Mix in foods that can help for burning fat and muscle toning.
In addition to a balanced diet that gives your body all of the nutrition it needs, there are a few specific foods that can actually help boost fat loss, which will improve your muscle tone.
Peppers, green tea, berries, and whole grains have been shown to help facilitate weight loss, so try adding them into your meals to reap their benefits.
Try to have at least 1 serving of fat-burning food a day.
Final Thought
Hop on a rowing machine, simply perform a basic rowing stroke, and tone every major muscle group of your body. Stay consistent with a healthy diet and exercise, you’ll improve your muscle tone and definition.
Enjoy your muscle toning voyage on the rower and row yourself to a healthy life.
Happy rowing!
For more rowing knowledge and product info about our Topiom water rowing machine, check here! We’re looking forward to having you back!


